Products serve as the cornerstone of both brands and retailers, constituting their essence and purpose. Companies thrive on the availability of products for sale, necessitating a meticulous orchestration of various operational aspects to bring these products to market effectively. Without a standardized approach, the absence of streamlined processes can result in hindrances and operational inefficiencies.
When it comes to product management, two indispensable software solutions utilized by retailers are Product Information Management and Product Lifecycle Management. However, despite their significance, these tools are frequently misconstrued. While both are integral to the seamless creation, promotion, and distribution of products, they diverge fundamentally in their functionalities and objectives.
Let’s explore more about PIM vs. PLM.
What is a Product Information Management?
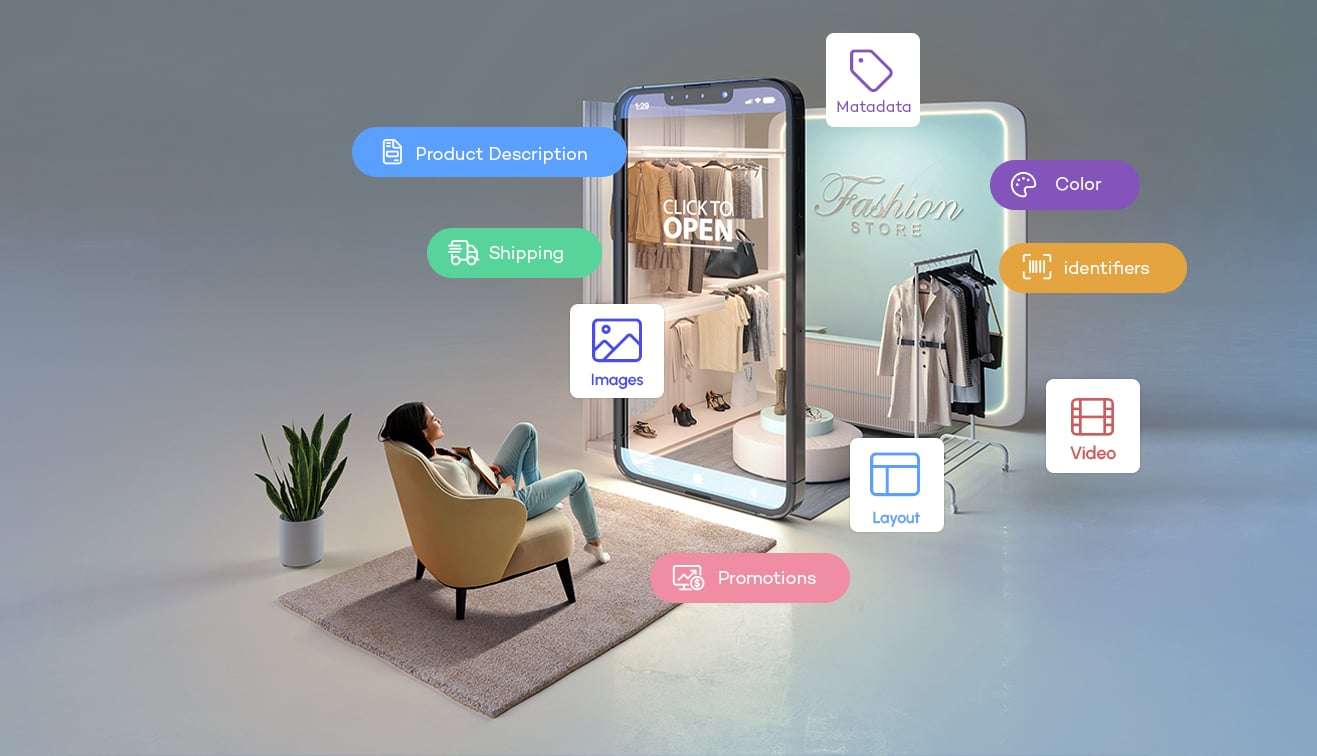
PIM stands for Product Information Management, a software solution designed to assist online enterprises such as retailers, brands, and manufacturers in centralizing and organizing product information. By utilizing PIM, businesses can efficiently store and manage product data, leading to notable reductions in time to market. Furthermore, PIM facilitates seamless integration with marketplaces and channels, enabling swift syndication of product information across various platforms.
Why is PIM Important?
The primary function of PIM is to gather, merge, refine, enhance, and simplify product data flow towards end-users. It serves as a centralized repository for all product-related information, ensuring smooth dissemination across multiple touchpoints to deliver enriched product experiences. PIM is dedicated to empowering marketing and sales efforts, focusing primarily on delivering comprehensive customer-facing product information.
What is a Product Lifecycle Management?
PLM, or Product Lifecycle Management, streamlines the comprehensive management of a product throughout its entire lifecycle. Consider a running shoe as an example: what customers see as the final product on an online store has traversed numerous stages before reaching its consumable form. Beginning as a conceptual sketch on a whiteboard during the ideation phase, the shoe evolves through design iterations and CAD models. Subsequently, it progresses through production, launching, and finally arrives at the market for consumer access.
According to Mordor Intelligence Report, the PLM market is estimated to reach $390 million in 2024 and is predicted to cross $672 by 2029, at a CAGR of 11.48%.
Why is PLM Important?
PLM's distinct responsibility lies in overseeing every facet of information pertinent to a product's lifecycle, excluding data intended for marketing or sales purposes. It encompasses details regarding product design, developmental stages, engineering alterations, project progression, compliance adherence, research and development, among others.
Contrary to managing customer-facing information, PLM concentrates solely on refining and optimizing product lifecycle operations.
PIM vs. PLM: Key Differences
Here are some key differences between PIM and PLM:
| Aspect | PIM | PLM |
| Product Lifecycle | Operates during the later stages of the product lifecycle. | Operates throughout the entire product lifecycle. |
| Collaboration and Workflow Management | Collaboration among sales, marketing, and content teams to ensure accurate and consistent product information. | Collaboration among cross-functional teams involved in product development, including design, engineering, manufacturing, and supply chain management. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Managing basic compliance information, such as product safety certifications and labeling requirements, particularly for consumer products. | Managing regulatory compliance throughout the product lifecycle, including tracking changes in regulations, documenting compliance testing results. |
| Primary Data Types | Descriptions, images, pricing, and more. | CAD files, specifications, BOM, and more. |
| Target Users | Marketing, sales, and e-commerce team. | Engineering, manufacturing, and R&D. |
| Integration | Integrated with e-commerce, CMS, ERPs. | Integrated with CAD, ERP, and MES. |
| Customer Benefit | Enhance product presentation. | Streamline design, product, and maintenance. |
| Business Objective | Improved sales and customer satisfaction. | Efficient product development and reduce time-to-market. |








































































.jpg?w=3840&q=75)


.png?w=3840&q=75)









.jpg?w=3840&q=75)